Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) has become an invaluable tool in detecting and preventing money laundering activities. With the rise of digital technologies, vast amounts of publicly accessible data are available to analysts and investigators to track and uncover suspicious financial activities. OSINT refers to the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of information from publicly available sources like websites, social media, public records, and other online databases.
How OSINT Aids in Detecting Money Laundering
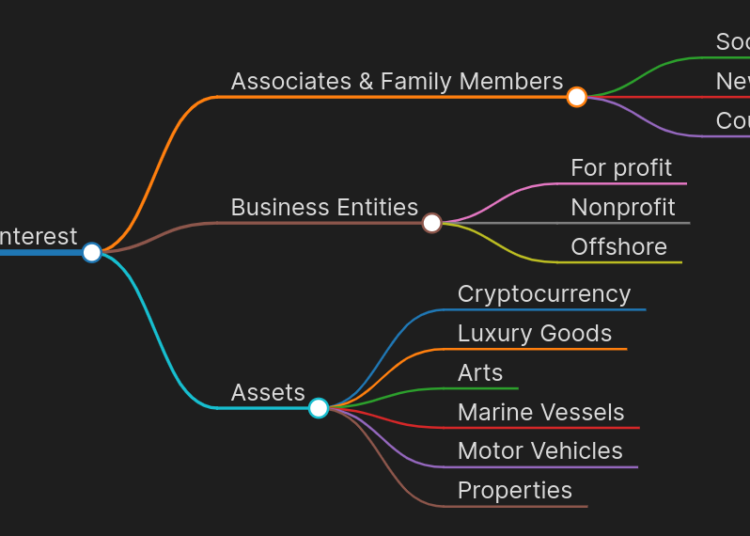
1. Tracing Beneficial Ownership
One of the biggest challenges in money laundering investigations is identifying the true owners of shell companies and complex corporate structures. Money launderers often use these entities to hide the origins of illicit funds. OSINT can be used to:
- Access corporate registries and databases to identify shareholders and directors of companies.
- Cross-reference ownership information across jurisdictions.
- Detect patterns where individuals or organizations control multiple entities that might be used to obscure financial flows.
Example: In 2023, investigators used OSINT tools to unearth the hidden ownership of multiple offshore shell companies linked to a large money laundering scheme operating out of Eastern Europe.
2. Monitoring Social Media for Red Flags
Social media platforms provide a wealth of information about individuals and organizations. Money launderers, despite their attempts to remain hidden, often leave digital footprints. OSINT can help identify:
- Lavish lifestyles that do not align with declared income sources.
- Connections between individuals or organizations with known criminals or suspicious actors.
- Public mentions of transactions, partnerships, or business activities that raise questions about their legitimacy.
Example: A 2022 investigation in South America used OSINT to track down a luxury car dealer who was using his business to launder drug money. His social media posts flaunting high-end cars and lavish purchases were inconsistent with the revenue of his business, leading to deeper scrutiny.
3. Analyzing Transaction Patterns and Cryptocurrency Wallets
OSINT tools can be used to analyze publicly available blockchain data and transaction records. While cryptocurrencies are often used in money laundering due to their perceived anonymity, blockchain technology leaves behind a permanent record of transactions. OSINT techniques can:
- Track suspicious cryptocurrency wallet activities.
- Identify patterns of frequent, small transactions that could signal structuring or smurfing (a technique used to avoid detection).
- Monitor exchanges and cryptocurrency ATMs for large or unexplained transactions.
Example: In 2021, a global task force used OSINT to analyze Bitcoin wallets associated with a dark web marketplace. By tracing patterns and connecting wallet addresses to public exchanges, they uncovered a network laundering millions in cryptocurrency.
4. Exploring Public Records and Databases
Publicly accessible databases, such as court records, financial reports, property ownership records, and tax filings, provide a wealth of information about individuals and organizations. OSINT investigators can:
- Look into inconsistencies in tax filings or financial statements that do not match an individual’s or company’s assets.
- Examine court records to identify any past involvement in criminal or fraudulent activities.
- Investigate property purchases or other high-value asset acquisitions that appear suspicious given the public financial profile of the individual or entity.
Example: In 2024, OSINT analysts uncovered a series of real estate transactions in New York linked to a money laundering operation. By reviewing publicly available property records, they identified over-inflated property purchases made through shell companies that were later traced to foreign political figures.
5. Cross-referencing Sanctions Lists and Watchlists
International sanctions lists, politically exposed persons (PEP) databases, and financial crime watchlists are often used in conjunction with OSINT to identify high-risk individuals and entities. Money launderers connected to criminal networks or corrupt regimes frequently appear on these lists. By cross-referencing individuals and organizations with these public databases, investigators can:
- Flag individuals or companies involved in suspicious transactions.
- Detect connections to entities already under scrutiny for financial crimes.
- Prevent financial institutions from engaging with blacklisted individuals or businesses.
Example: In 2022, a European bank used OSINT to identify a potential client on an international sanctions list. After investigating the client’s corporate history and connections, they uncovered a network of shell companies designed to launder money through the bank.
6. Using OSINT Tools for Data Analysis and Visualization
Specialized OSINT tools like Maltego, SpiderFoot, and public record crawlers allow investigators to visualize relationships between entities, track complex financial flows, and build connections between individuals, organizations, and assets. These tools can:
- Map out networks of companies, accounts, and individuals involved in money laundering schemes.
- Uncover hidden connections and cross-border activities that might be missed by traditional investigative methods.
- Provide a clear picture of how money is being moved and laundered across different jurisdictions.
Example: Investigators used Maltego in a 2023 probe into an international money laundering ring. The tool helped visualize the relationships between several offshore companies, eventually exposing a scheme to launder drug profits through art auctions.